Google Storage Decision Chart
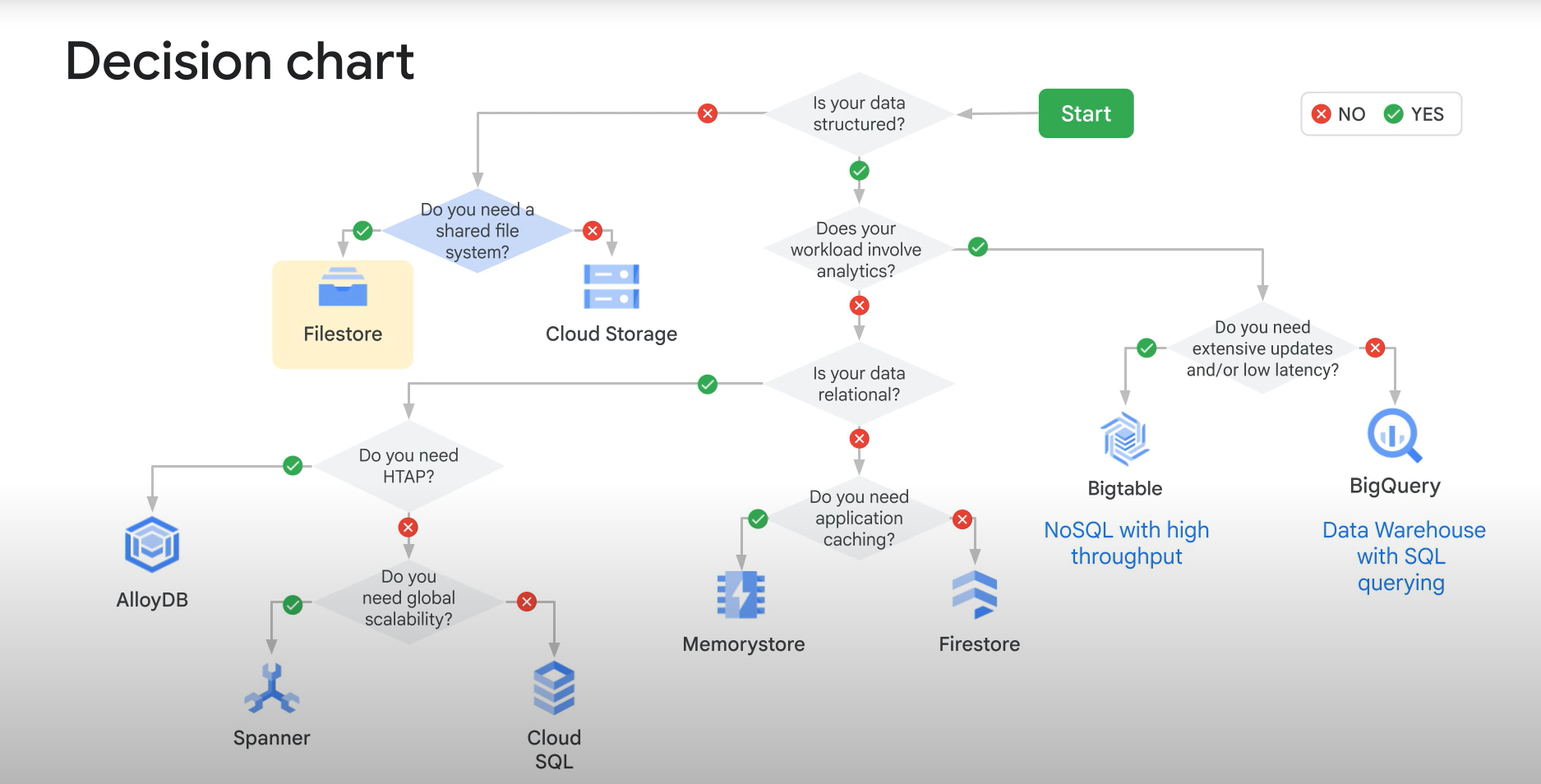
Choosing the right Google Storage service for your use case can be a daunting task. Google offers a wide range of services that perfectly fit various use cases. The decision chart above provides a clear path to selecting the optimal storage solution.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the decision process:
1. Structured vs. Unstructured Data
The first question to ask is whether your data is structured.
Unstructured Data
If your data is not structured (e.g., media files, backups, logs), you have two main options based on your need for a shared file system:
- Filestore: Choose this if you need a high-performance shared file system (NFS) for your applications.
- Cloud Storage: Choose this for object storage. It is ideal for storing unstructured data like images, videos, and backups, offering high durability and availability.
Structured Data
If your data is structured, the next step is to determine the nature of your workload.
2. Analytics vs. Transactional Workloads
Does your workload involve analytics?
Analytics Workloads
If your primary goal is analytics, consider the latency and update requirements:
- Bigtable: Choose this if you need extensive updates and/or low latency. It is a NoSQL database designed for high throughput and scalability, perfect for time-series data and ad-tech.
- BigQuery: Choose this if you do not need low latency updates. It is a serverless, highly scalable Data Warehouse aimed at SQL querying and analyzing large datasets.
Transactional/Operational Workloads
If your workload is not focused on analytics (i.e., it’s operational), the next question is whether your data is relational.
3. Relational Data
If your data is relational (SQL), you have three paths:
- AlloyDB: Choose this if you need HTAP (Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing). It provides a fully managed PostgreSQL-compatible database service for demanding enterprise workloads.
- Spanner: Choose this if you need global scalability. Spanner is a fully managed, mission-critical, relational database service that offers transactional consistency at a global scale.
- Cloud SQL: Choose this if you do not need global scalability. It is a fully managed relational database service for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
4. Non-Relational Data
If your data is not relational (NoSQL) and not for analytics:
- Memorystore: Choose this if you need application caching. It provides a fully managed in-memory data store service for Redis and Memcached.
- Firestore: Choose this if you do not need caching. It is a flexible, scalable NoSQL cloud database for storing and syncing data for client- and server-side development (mobile, web, and server).